Blog
Battery Cell vs Module vs Pack: What’s the Difference?
2026-02-20 | Eric
Understanding the difference between a battery cell, module, and pack is essential when selecting or designing a lithium battery system. Whether for electric vehicles, solar energy storage, backup power, or industrial applications, each structural level plays a distinct and critical role in performance, safety, and scalability.
This guide explains how battery cells, modules, and packs differ — and how they work together to deliver reliable energy solutions.
Introduction to Battery Structure
Modern lithium battery systems are built using a hierarchical structure:
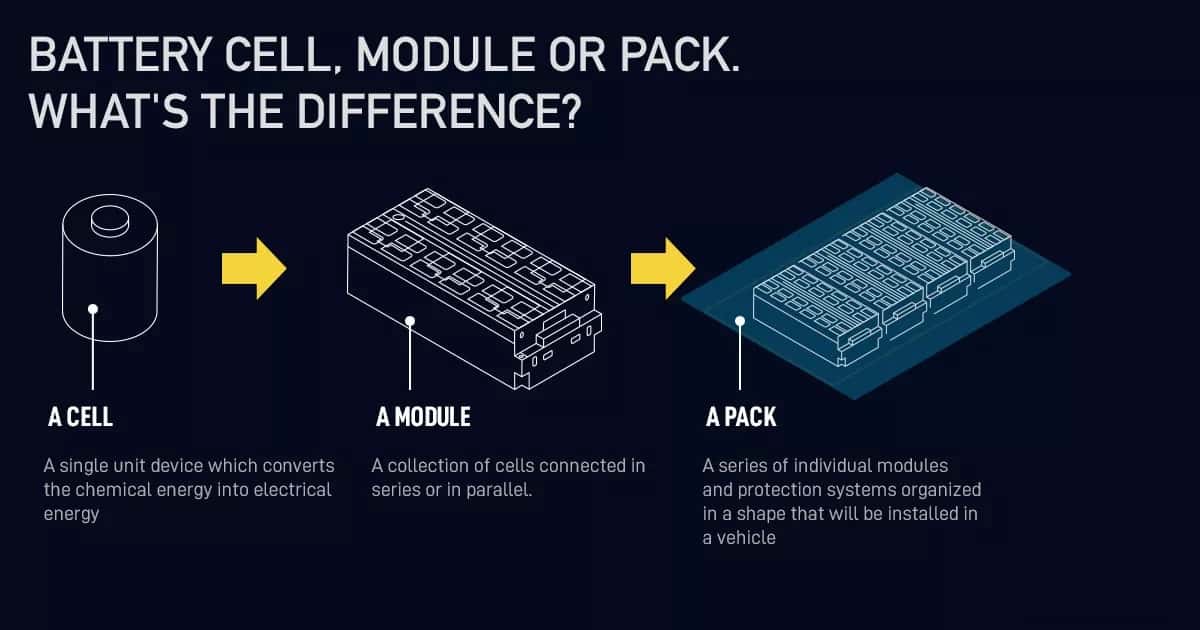
Battery Cell → Battery Module → Battery Pack
Each level increases power, voltage, and system complexity. This modular design allows manufacturers to scale energy storage systems from small portable devices to large industrial and renewable energy installations.
What Is a Battery Cell?
A battery cell is the smallest and most fundamental electrochemical unit in a battery system. It converts chemical energy into electrical energy through controlled chemical reactions.
In lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) systems, a single cell typically provides a nominal voltage of 3.2V.
Common Types of Lithium Battery Cells
- Cylindrical Cells
Known for durability and consistent manufacturing quality. Widely used in power tools and electric vehicles. - Prismatic Cells
Space-efficient and structurally stable. Common in energy storage systems and EV battery modules. - Pouch Cells
Lightweight and flexible in design, suitable for applications where weight reduction is critical.
Key Technical Parameters of a Battery Cell
- Capacity (Ah) – Indicates how much charge a cell can store.
- Nominal Voltage (V) – Determines electrical potential output.
- Energy Density (Wh/kg or Wh/L) – Defines how much energy is stored per unit weight or volume.
- Cycle Life – The number of charge/discharge cycles before capacity significantly degrades.
- Internal Resistance – Affects heat generation and efficiency.
High-quality cells are the foundation of a reliable battery system. Poor cell consistency can compromise the entire pack’s performance and lifespan.
What Is a Battery Module?
A battery module is created by connecting multiple battery cells together in a structured assembly. Modules increase voltage and/or capacity to meet higher power demands while improving safety and manageability.
Series vs Parallel Configuration
- Series Connection
Increases voltage.
Example: Four 3.2V LiFePO4 cells connected in series produce 12.8V. - Parallel Connection
Increases capacity (Ah) while maintaining voltage.
Most modules combine both configurations to achieve a balanced output for specific applications.
Key Features of Battery Modules
- Cell Balancing – Ensures uniform voltage across cells
- Structural Reinforcement – Mechanical housing protects cells
- Thermal Control Design – Improves heat dissipation
- Integrated Monitoring (Optional) – Some modules include basic monitoring systems
Modules enhance system reliability by grouping cells into manageable subunits. This approach improves maintainability and reduces safety risks.
What Is a Battery Pack?
A battery pack is the complete, application-ready energy storage system. It integrates multiple modules along with advanced control and safety systems.
Battery packs are engineered for specific voltage, capacity, and environmental requirements.
Core Components of a Battery Pack
- Battery Modules – Configured in series and parallel
- Battery Management System (BMS) – Monitors voltage, temperature, State of Charge (SoC), and State of Health (SoH)
- Thermal Management System – Air-cooled or liquid-cooled solutions
- Protective Enclosure – IP-rated housing for dust, moisture, and impact resistance
- Safety Protection Circuits – Overcurrent, overvoltage, short-circuit protection
The BMS acts as the “brain” of the battery pack, ensuring operational safety and maximizing service life.
How Cells, Modules, and Packs Work Together
The relationship is hierarchical and scalable:
- Cells provide fundamental energy storage.
- Modules organize cells into higher-capacity building blocks.
- Packs integrate modules into a complete, intelligent energy solution.
This architecture allows manufacturers to design customized lithium battery systems for different industries without redesigning from scratch.
Applications of Battery Packs
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
High-voltage battery packs power electric drivetrains and determine driving range and performance.
Solar Energy Storage
Lithium iron phosphate battery packs store excess solar power for residential or commercial use.
Backup Power Systems (UPS)
Reliable battery packs ensure uninterrupted power supply in critical infrastructure.
Industrial and Off-Grid Systems
Custom battery packs support telecom towers, marine systems, RVs, and off-grid installations.
Key Design Considerations in Battery Systems
1. Thermal Management
Excessive heat accelerates degradation and reduces cycle life. Proper cooling design ensures stable long-term performance.
2. Battery Management System (BMS)
A high-quality BMS enhances safety, extends lifespan, and optimizes performance by continuously monitoring each cell.
3. Safety Engineering
Protection against short circuits, overcharging, and thermal runaway is essential for high-energy lithium systems.
4. Energy Efficiency
Optimized electrical connections and material selection reduce energy losses and improve overall system efficiency.
Why Cell Quality Determines System Reliability
In lithium battery systems — especially LiFePO4 battery packs — performance consistency starts at the cell level. Even minor variations in internal resistance or capacity can lead to imbalance, heat generation, and long-term degradation.
Choosing high-grade cells and implementing strict quality control is critical for achieving:
- Long cycle life
- Stable voltage output
- Enhanced safety
- Lower total cost of ownership
Conclusion
The difference between a battery cell, module, and pack lies in scale, function, and system integration.
Cells store energy.
Modules organize and scale it.
Packs deliver it safely and intelligently to real-world applications.
Understanding this structure is essential when selecting lithium battery solutions for solar storage, EV systems, or industrial applications.
As demand for reliable and efficient energy storage continues to grow, advanced LiFePO4 battery systems will play a central role in powering the future.
Popular Articles
Contact Details
Worktime :Monday to Friday 9am - 6pm (HKT)
WhatsApp/Wechat/Mobile :+8613645616165
Email : info@lifepo4cellstore.com
