Blog
Functions and Applications of Battery Management Systems (BMS)
2025-12-31 | Eric
In the rapid evolution of modern technology, battery technology has become a core enabler of various innovative applications. From electric vehicles (EVs) to smartphones, and renewable energy storage systems, the widespread use of batteries is driving societal progress. However, as battery technology becomes more complex and its applications diversify, effectively and safely managing batteries has become an urgent challenge. This is where the Battery Management System (BMS) plays a crucial role. BMS not only enhances the performance and lifespan of batteries but also ensures safety during their operation. In this article, we will explore the definition, functions, and key roles of BMS in modern technology, aiming to provide a comprehensive understanding of this essential technology.
Overview of Battery Management System (BMS)
Definition and Core Functions:
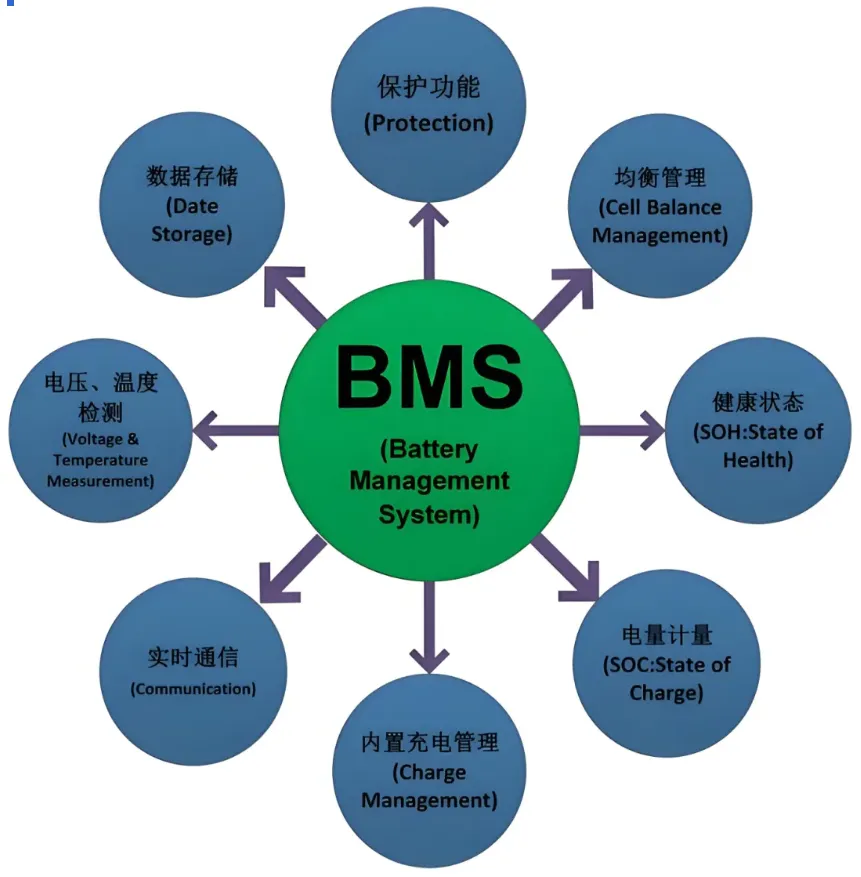
A Battery Management System (BMS) is an electronic system designed to monitor and manage the operation of rechargeable batteries, whether single cells or battery packs. The primary functions of a BMS include protecting the battery from operating outside its safe limits, monitoring the battery's voltage, temperature, and current in real-time, reporting relevant data, controlling the battery’s working environment, and ensuring battery balance. By performing these tasks, BMS ensures the safe, stable, and efficient operation of battery systems.
BMS is particularly essential in complex or large battery systems, including electric vehicles, energy storage systems, and other high-performance battery applications. Its main tasks include safety protection, charge/discharge management, and information monitoring, thereby improving battery performance, extending its lifespan, and preventing potential safety risks.
The Purpose of a BMS
In complex battery systems, the BMS is a vital component. Acting as a bridge between the battery and other systems, BMS handles key aspects like battery voltage, temperature, charge/discharge status, and real-time monitoring. These functions include:
- Safety Protection: Prevents overcharging, overdischarging, and overheating.
- Charge Balancing: Ensures the batteries charge and discharge uniformly.
- Environmental Control: Regulates the temperature and conditions in which the battery operates.
- Data Generation and Transmission: Provides real-time feedback to users or connected systems for optimal performance.
Without a BMS, batteries can suffer from overcharging or deep discharge, which may cause chemical reactions to spiral out of control, leading to overheating, thermal runaway, or even explosions. Furthermore, imbalances in the battery pack can accelerate aging, reduce performance, and increase maintenance costs. In severe cases, such imbalances may lead to safety hazards like fires, posing risks to both users and equipment.
By integrating a BMS, battery health can be effectively assessed, preventing overcharging and deep discharge, balancing charge levels, and providing clear status information to ensure safe operation and prolong battery life.
Evolution of Battery Management Systems (BMS)
The research and development of BMS have been led by countries like the United States, Germany, and Japan. The concept of BMS dates back to the 1970s with the rise of battery technology. However, it wasn’t until the 1990s—along with the development of electric vehicles—that BMS began to receive widespread attention. The United States pioneered early BMS models, propelling technological advancements in the field. Germany expanded BMS applications with systems like BATTMAN and Bosch’s cloud-based battery management, which extended battery life and broadened the system’s capabilities. Meanwhile, Japan supported the growth of electric vehicles and the widespread use of BMS through government policies.
BMS has evolved from basic protection circuits to more advanced smart management systems. Key developments include:
- Advanced Monitoring Features: Modern BMS systems can monitor battery voltage, temperature, charge status, and health in real-time, offering precise data analysis and early fault warnings.
- Improved Balancing Technologies: Active and passive balancing technologies have been introduced, improving the overall performance and lifespan of battery packs by ensuring uniform charge distribution.
- Enhanced Communication and Data Management: Support for advanced communication protocols (e.g., CAN Bus, Modbus) allows seamless integration with vehicles or other systems, optimizing data transfer and management.
- Integrated Design: Modern BMS systems typically integrate additional features such as thermal management, charging control, and safety protection, reducing system complexity and enhancing reliability.
- Smart Algorithms: Advanced algorithms are now employed to optimize charge/discharge strategies, predict battery life, and enhance system efficiency and safety.
- Remote Monitoring and Cloud Technologies: Through remote monitoring and cloud computing, BMS can track battery status in real-time, enabling remote diagnostics and maintenance.
- AI Integration: The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and large models boosts BMS’s predictive capabilities. AI algorithms leverage historical data and real-time monitoring to predict battery health, optimize charge/discharge strategies, and anticipate potential failures or hazardous conditions.
These advancements have transformed BMS from a simple protection system to an intelligent, highly efficient battery management solution, catering to the increasingly complex needs of modern battery systems.
Applications of Battery Management Systems (BMS)
BMS is indispensable in any application involving complex battery systems. Key application areas include:
- Electric and Hybrid Vehicles (EVs/HEVs): BMS in EVs and HEVs manage the battery pack, ensuring optimal performance and preventing overcharging or deep discharge. It monitors key parameters like temperature, current, voltage, and state of charge (SoC) to extend battery life and maintain safety.
- Renewable Energy Systems (Solar, Wind, etc.): In renewable energy systems, BMS manages energy storage and distribution. It optimizes the performance of storage systems, ensuring maximum energy storage and availability when needed.
- Energy Storage Systems (Residential, Commercial, Grid-scale): In energy storage systems, BMS monitors and controls charge/discharge cycles, ensuring efficient energy use and extending battery life.
- Industrial and Marine Applications: BMS is used in industrial and marine settings to manage large-scale battery systems, ensuring performance, reliability, and safety. It monitors parameters like temperature, voltage, and current to protect batteries from potential hazards.
- Telecommunications and Data Center Backup Systems: In backup power systems for telecoms and data centers, BMS ensures that batteries are always in optimal condition and ready to supply power when needed, monitoring health status and charge levels to maintain reliable performance.
- Large Capacity Mobile Power Systems: Used in outdoor or emergency power supplies, these systems, often called home energy storage, rely on BMS to manage multiple battery packs, ensuring stable and reliable power delivery in emergencies while extending battery lifespan.
- Electric Tools: In power tools, BMS helps ensure stable battery operation under high load conditions, preventing over-discharge or overheating and enhancing the tool’s and battery’s longevity.
- Two-Wheeled Vehicles: For electric bicycles and scooters, BMS is crucial in managing the battery pack, optimizing range and safety while ensuring stable output in various riding conditions.
- Robotics: In industrial, service, and consumer robots, BMS ensures reliable and safe battery management, optimizing energy use and supporting continuous operation in demanding environments.
Conclusion
The Battery Management System (BMS) is a pivotal technology for ensuring the safe, efficient, and long-lasting performance of batteries in numerous applications. As the demand for reliable and high-performance batteries grows across sectors—from electric vehicles to renewable energy storage and industrial systems—BMS will continue to evolve, incorporating new technologies like AI, cloud computing, and advanced algorithms. Whether for personal or industrial use, a well-managed battery system ensures sustainability, safety, and performance, making BMS a key enabler of the future.
Popular Articles
Contact Details
Worktime :Monday to Friday 9am - 6pm (HKT)
WhatsApp/Wechat/Mobile :+8613645616165
Email : info@lifepo4cellstore.com
