Blog
Understanding the Difference Between On-Board and Off-Board Electric Vehicle Chargers
2025-12-06 | Eric
As the electric vehicle (EV) market continues to grow, understanding the various types of chargers and their functions is crucial for both consumers and industry professionals. Two of the most common types of EV chargers are on-board chargers and off-board chargers. While both serve the same fundamental purpose—charging the power battery of an EV—there are notable differences in their design, functionality, and usage. This article explores these differences, helping consumers and businesses make informed decisions.
What is an On-Board Charger?
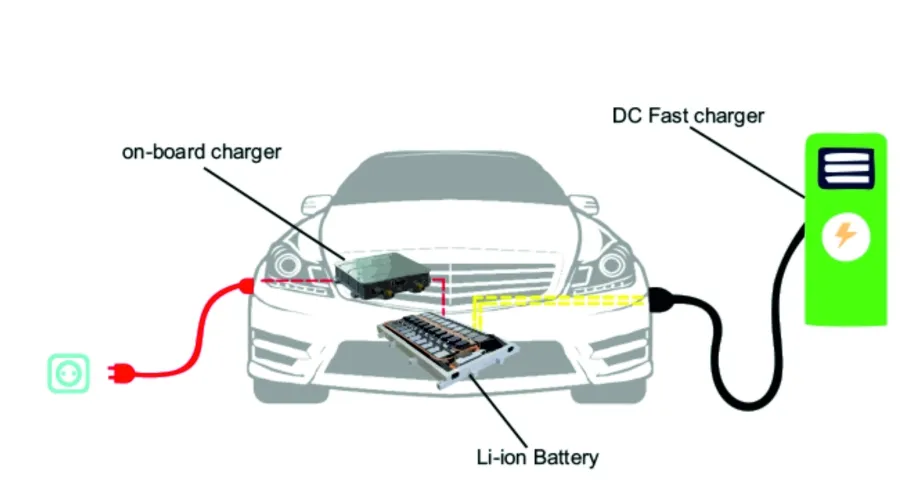
An on-board charger (OBC) is a device installed inside the electric vehicle (EV). Its primary function is to convert AC (alternating current) from an external power source, such as a wall outlet, into DC (direct current) that can be stored in the vehicle’s battery.
Key Features of On-Board Chargers:
- Compact and Lightweight: Since the on-board charger is installed within the vehicle, it must be small, lightweight, and space-efficient. This makes it ideal for everyday charging at home or public charging stations.
- AC to DC Conversion: The on-board charger converts AC power from an external socket (e.g., 220V AC or 380V AC) into the DC power required for the vehicle’s battery.
- Dynamic Charging Control: On-board chargers communicate with the battery management system (BMS) to regulate the voltage and current levels, ensuring safe and efficient charging.
Pros of On-Board Chargers:
- Convenience: On-board chargers can be plugged into any standard AC outlet, making them convenient for home charging and accessible in locations with AC power.
- Battery Longevity: Slow charging (typical of on-board chargers) is gentler on the battery, helping to prolong its life.
Cons of On-Board Chargers:
- Slow Charging: Due to size and power limitations, on-board chargers typically provide a lower current and slower charging speeds, resulting in longer charging times.
- Lower Power Capacity: The charging power is relatively low, meaning that the vehicle may take several hours to fully charge, depending on the battery capacity.
What is an Off-Board Charger?
An off-board charger, on the other hand, is external to the electric vehicle and typically installed at a fixed location like a charging station or in a public space. It is connected to the AC power grid and is responsible for converting AC power into DC power for the vehicle.
Key Features of Off-Board Chargers:
- High Power Capacity: Unlike on-board chargers, off-board chargers are not constrained by the vehicle's limited space. As a result, they can provide much higher power levels, enabling faster charging speeds.
- DC Fast Charging: Off-board chargers are often referred to as DC chargers because they deliver high-voltage DC power directly to the vehicle's battery, bypassing the vehicle's internal conversion system.
- External Installation: These chargers are typically fixed in public or private locations, such as charging stations or fleet depots.
Pros of Off-Board Chargers:
- Faster Charging: Off-board chargers deliver much higher power, allowing for rapid charging (often called "fast charging"). This is ideal for commercial fleets or long-distance travelers who need to quickly recharge their vehicles.
- More Efficient for Large Vehicles: Off-board chargers can handle higher loads and are typically used for charging larger EVs or fleets that require faster turnaround times.
Cons of Off-Board Chargers:
- High Initial Cost: The power and infrastructure required for off-board chargers make them expensive to install and maintain. This can lead to higher construction costs for charging stations.
- Immobility: Unlike on-board chargers, which can charge a vehicle anywhere there’s an AC outlet, off-board chargers are stationary and can only be accessed at fixed locations. This can limit their accessibility in rural or underserved areas.
- Battery Wear: While fast charging is convenient, frequent use of high-power off-board chargers can reduce the lifespan of an EV’s battery.
Key Differences Between On-Board and Off-Board Chargers
| Feature | On-Board Charger | Off-Board Charger |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Installed inside the vehicle | Installed outside the vehicle |
| Size & Weight | Compact, light | Large, heavy |
| Power Supply | AC to DC (typically lower power) | AC to DC (high power, fast charging) |
| Charging Speed | Slow (typically “slow charging”) | Fast (DC fast charging) |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher installation cost |
| Battery Impact | Prolongs battery life (slow charging) | Frequent fast charging can reduce battery lifespan |
| Portability | Portable (can charge anywhere with AC outlet) | Stationary (fixed location) |
Which Charger Is Right for You?
The decision between an on-board charger and an off-board charger largely depends on your specific needs and usage patterns:
- For daily commuters and personal EV owners, on-board chargers are often sufficient. They offer the convenience of home charging and tend to have a lesser impact on the battery's long-term health.
- For businesses, fleet operators, or those who need quick recharging, off-board chargers provide the advantage of speed and efficiency. Public charging stations and commercial fleets benefit from the high power and rapid charging capabilities of off-board chargers.
Conclusion
Both on-board chargers and off-board chargers play essential roles in the growing EV ecosystem, each catering to different needs. Understanding the benefits and drawbacks of each can help you make an informed choice when considering the best solution for your electric vehicle charging needs.
Popular Articles
Contact Details
Worktime :Monday to Friday 9am - 6pm (HKT)
WhatsApp/Wechat/Mobile :+8613645616165
Email : info@lifepo4cellstore.com
