Blog
LiFePO4 Battery Float Voltage Settings and Optimization: The Ultimate Guide (2026)
2026-02-07 | Eric
LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries have become a preferred choice for solar energy storage, electric vehicles, RV systems, marine applications, and backup power solutions due to their excellent safety profile, long cycle life, and stable performance.
However, one of the most common configuration challenges users face is selecting the correct LiFePO4 battery float voltage. Incorrect float voltage settings can gradually reduce battery lifespan, even if no immediate failure occurs.
Based on practical system testing across multiple solar and off-grid installations, this guide explains:
- What float voltage means for LiFePO4 batteries
- Optimal float voltage ranges
- How to configure and maintain correct settings
- How LiFePO4 compares to other battery chemistries
What Is a LiFePO4 Battery?
LiFePO4 batteries are a lithium-based battery chemistry known for thermal stability, long cycle life (3,000–6,000+ cycles), and high safety margins. Compared to conventional lithium-ion or lead-acid batteries, LiFePO4 batteries are far less prone to thermal runaway, swelling, or fire.
These characteristics make LiFePO4 batteries ideal for:
- Solar and energy storage systems
- Electric vehicles and mobility platforms
- Marine and RV power systems
- Telecom and residential backup power
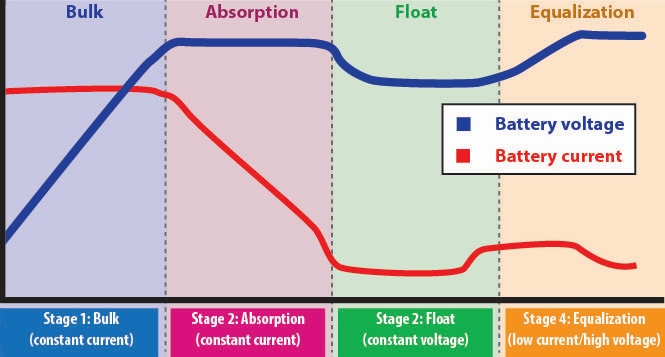
What Is Float Voltage and Why It Matters
Float voltage refers to the voltage level applied to a battery after it has reached full charge, maintaining the battery at 100% state of charge without overcharging.
For LiFePO4 batteries, float voltage is especially important because:
- Excess voltage accelerates cell aging
- Prolonged high voltage increases internal resistance
- Incorrect settings reduce usable cycle life over time
While LiFePO4 chemistry is more tolerant than lead-acid batteries, float voltage should still be carefully optimized for long-term reliability.
Recommended LiFePO4 Battery Float Voltage Settings
Based on manufacturer specifications and field testing:
- Per cell float voltage:
3.20V – 3.30V - 12.8V (4S) LiFePO4 battery pack:
12.8V – 13.2V
This range maintains cell stability while avoiding unnecessary stress. Unlike lead-acid batteries, LiFePO4 batteries do not require aggressive float charging to remain healthy.
How Incorrect Float Voltage Affects LiFePO4 Batteries
Float Voltage Too High
- Accelerated capacity degradation
- Increased heat generation
- Reduced cycle life
- Potential safety risks under extreme conditions
Float Voltage Too Low
- Battery remains undercharged
- Reduced runtime and efficiency
- Inconsistent system performance
Maintaining the correct LiFePO4 battery float voltage ensures maximum lifespan and predictable performance.
How to Set LiFePO4 Float Voltage Correctly
To configure float voltage accurately:
- Use a LiFePO4-compatible charger or inverter
- Follow battery manufacturer specifications
- Set float voltage with precision (±0.02V preferred)
- Adjust for ambient temperature when necessary
- Verify voltage using a calibrated multimeter after resting the battery for several hours
Regular verification helps detect configuration drift or equipment issues early.
Key Factors That Influence Float Voltage
Several variables affect optimal float voltage performance:
- Temperature: Higher temperatures require slightly lower float voltage
- Charging current: High current may cause temporary voltage spikes
- Battery age and SOH: Aging cells respond differently
- Cell balance: Poorly balanced cells reduce pack stability
Monitoring these factors ensures consistent long-term operation.
Safety Considerations
- Always use chargers and BMS designed specifically for LiFePO4 batteries
- Avoid using lead-acid charging profiles
- Charge in well-ventilated environments
- Inspect for abnormal heat, swelling, or voltage irregularities
Proper float voltage settings significantly reduce operational risk.
LiFePO4 vs Other Battery Types
| Battery Type | Float Voltage (Per Cell) | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Lead-Acid | 2.25V – 2.30V | High maintenance, sensitive to overcharge |
| Ternary Lithium | 4.1V – 4.2V | High energy density, lower safety margin |
| LiFePO4 | 3.2V – 3.3V | High safety, long lifespan, stable |
Maintenance Best Practices
- Check float voltage regularly
- Avoid deep discharge below 2.5V per cell
- Operate within 0°C–45°C when possible
- Store batteries at ~50% SOC for long periods
Consistent maintenance maximizes return on investment.
FAQ
What happens if float voltage is too high?
It accelerates aging and reduces cycle life.
Can I use a lead-acid charger?
No. Charging profiles differ and may damage LiFePO4 batteries.
How often should float voltage be checked?
Monthly, especially during the first few months.
Is over-discharge acceptable?
No. Repeated deep discharge permanently reduces capacity.
Can LiFePO4 be charged below 0°C?
Only with appropriate low-temperature protection.
Conclusion
Optimizing LiFePO4 battery float voltage is essential for achieving maximum safety, efficiency, and lifespan. By applying the correct voltage range, using compatible equipment, and monitoring environmental factors, LiFePO4 batteries can deliver reliable performance for years.
Popular Articles
Contact Details
Worktime :Monday to Friday 9am - 6pm (HKT)
WhatsApp/Wechat/Mobile :+8613645616165
Email : info@lifepo4cellstore.com
