Blog
The Ultimate Guide to 3.7V Rechargeable Batteries
2026-01-18 | Eric
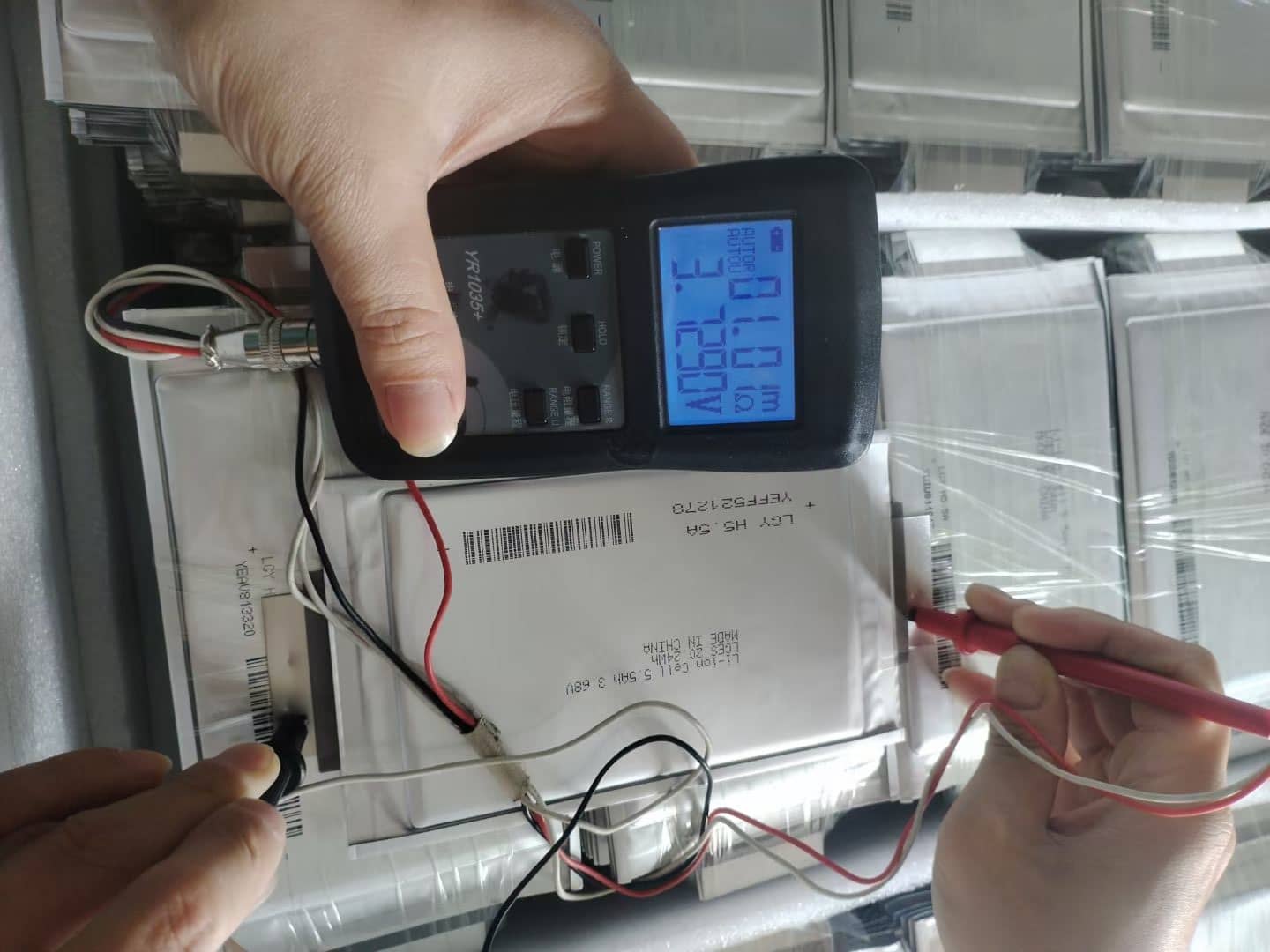
In the landscape of modern portable energy, the 3.7V rechargeable battery stands as the industry standard. From powering high-drain industrial tools to sleek consumer electronics, these lithium-based cells offer the optimal balance of energy density and weight.
Whether you are a procurement professional sourcing components or a tech enthusiast building a custom project, understanding the nuances of 3.7V chemistry is critical for safety and performance.
1. What is a 3.7V Rechargeable Battery?
A 3.7V battery is a lithium-based secondary (rechargeable) cell. The "3.7V" refers to its nominal voltage—the average voltage the battery maintains during its discharge cycle.
The Internal Architecture
High-performance 3.7V cells, typically utilizing Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) or Lithium-Polymer (Li-Po) chemistries, consist of four primary components:
- Anode (Negative): Generally constructed from high-grade graphite.
- Cathode (Positive): Composed of lithium metal oxides (e.g., $LiCoO_2$ or $LiNiMnCoO_2$).
- Electrolyte: A lithium salt in an organic solvent that facilitates ion transport.
- Separator: A critical safety component that prevents internal short circuits while allowing ions to pass.
2. 3.7V Battery Types: Li-ion vs. Li-Po
While both share the same nominal voltage, their physical and chemical properties dictate their use cases.
| Feature | Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) | Lithium-Polymer (Li-Po) |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | High | Slightly Lower |
| Form Factor | Rigid, mostly cylindrical | Flexible, thin, and flat |
| Durability | High (Robust metal casing) | Fragile (Pouch format) |
| Common Uses | Laptops, EVs, Flashlights | Drones, Smartphones, RC Hobby |
3. Standardized Sizes and Form Factors
Unlike primary AA/AAA batteries, 3.7V rechargeable batteries come in varied dimensions, particularly in the Li-ion category where names reflect their physical measurements.
Cylindrical Li-ion Standards
The naming convention follows a simple rule: First two digits = Diameter (mm), Next three digits = Length (mm).
- 18650: The "Gold Standard." Used in everything from Tesla Powerwalls to high-end flashlights.
- 21700: The emerging favorite for high-capacity applications (EVs and power tools) due to higher energy density.
- 14500: Identical in size to a standard AA battery but with significantly higher voltage.
- 26650: A high-capacity, high-drain cell often used in industrial equipment.
Pouch Li-Po Sizes
Li-Po batteries are customized by capacity (mAh). Because they lack a rigid shell, they can be manufactured in almost any dimension to fit specific device footprints, such as ultra-thin tablets.
4. Understanding the Voltage Curve: Charging and Discharge
A 3.7V battery is rarely exactly 3.7 volts. Its state of charge (SoC) is determined by its current voltage.
- Fully Charged: 4.2V. Exceeding this is dangerous and can lead to thermal runaway.
- Nominal Voltage: 3.7V. The mid-point of the discharge cycle.
- Discharged (Dead): 3.0V. While some cells can drop to 2.5V, most protection circuits (BMS) cut off at 3.0V to prevent permanent chemical damage.
Technical Pro-Tip: Charging follows the CC/CV (Constant Current / Constant Voltage) protocol. The charger provides a steady current until the battery hits 4.2V, then maintains that voltage while the current tapers off to zero.
5. Lifespan and Degradation Factors
A 3.7V battery's life is measured in cycles (one full charge and discharge).
- Li-ion: 300–500 cycles (Standard) | 1,000+ (Premium/LFP variants).
- Li-Po: 200–300 cycles.
Factors that "Kill" Your Battery:
- Deep Discharge: Frequently dropping below 2.5V causes copper shunts to form, leading to short circuits.
- Heat: Operating above 45°C (113°F) accelerates chemical decomposition.
- High Discharge Rates: Drawing more current than the battery's "C-rating" causes internal stress.
6. Professional Maintenance and Storage
To maximize ROI on your battery assets, follow these industry-standard protocols:
- The 50% Rule for Storage: If storing for more than 30 days, keep the battery at 3.8V (approx. 50% charge). Storing at 100% or 0% charge causes rapid capacity loss.
- Temperature Control: Store in a cool, dry environment (15°C to 25°C). Avoid "cold-soaking" batteries in sub-zero temperatures, which increases internal resistance.
- Smart Charging: Use a dedicated Li-ion charger with a built-in Battery Management System (BMS) to prevent overcharging and balancing issues.
7. Safety and Environmental Responsibility
3.7V batteries contain valuable but hazardous materials like Cobalt and Lithium.
- Recycling: Never dispose of these in standard waste. They represent a fire hazard in garbage trucks. Use dedicated lithium recycling programs to recover rare earth metals.
- Physical Inspection: If a battery shows "swelling" (common in Li-Po) or a "sweet" chemical smell, stop using it immediately. These are signs of internal gas buildup and imminent failure.
Conclusion
Selecting the right 3.7V battery requires balancing capacity (mAh), discharge rate (A), and physical size. For industrial applications, always prioritize cells from reputable manufacturers with certified UL or IEC testing.
Whether you need bulk 18650 cells for a production line or custom Li-Po packs for specialized hardware, our engineering team is here to help.
Popular Articles
Contact Details
Worktime :Monday to Friday 9am - 6pm (HKT)
WhatsApp/Wechat/Mobile :+8613645616165
Email : info@lifepo4cellstore.com
