Blog
Understanding C-Rate: The Key to Battery Performance
2025-12-08 | Eric
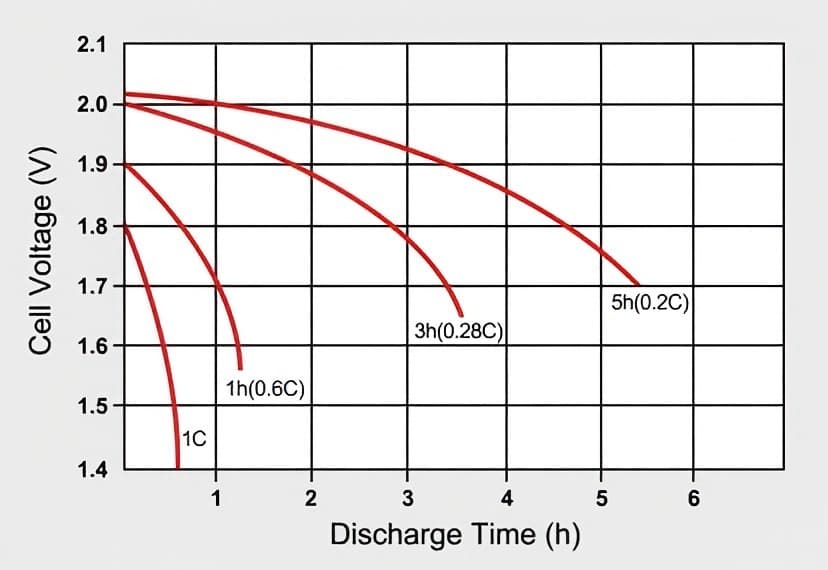
Table of Contents
- What is C-Rate?
- C-Rate and Battery Performance
- How Does C-Rate Affect Battery Capacity?
- Why Are Low C-Rates Used for Testing?
- The Impact of C-Rate on Battery Types
- How to Choose the Right C-Rate for Your Needs
- Conclusion
When it comes to batteries, the C-rate is one of the most crucial specifications for understanding their performance. It dictates how quickly a battery can be charged or discharged, which directly impacts its efficiency, lifespan, and application. Whether you're using batteries in electric vehicles, consumer electronics, or industrial equipment, understanding C-rates is essential for optimizing battery use.
What is C-Rate?
The C-rate refers to the speed at which a battery is charged or discharged relative to its maximum capacity. It is commonly used to describe the charging and discharging rates for different types of batteries. The concept helps to standardize battery performance, ensuring users understand how long a battery will last at specific rates of energy output.
For example, a 1Ah (amp-hour) battery rated at 1C means it should provide 1 amp of current for one hour. However, when the C-rate changes, so does the battery’s performance, impacting both the charge time and discharge time.
C-Rate and Battery Performance
- 1C Rate: A fully charged 1Ah battery discharging at a 1C rate will deliver 1A of current for 1 hour.
- 0.5C Rate: A 0.5C rate means the battery will provide 500mA for 2 hours.
- 2C Rate: At 2C, the battery will discharge at 2A for 30 minutes.
| C-Rate | Discharge Time |
|---|---|
| 5C | 12 minutes |
| 2C | 30 minutes |
| 1C | 1 hour |
| 0.5C or C/2 | 2 hours |
| 0.2C or C/5 | 5 hours |
| 0.1C or C/10 | 10 hours |
| 0.05C or C/20 | 20 hours |
Table 1: Typical discharge times at various C-rates for a 1Ah (1,000mAh) battery.
How Does C-Rate Affect Battery Capacity?
Battery capacity is the amount of energy a battery can store and deliver over time. To determine a battery’s true capacity, manufacturers often use a battery analyzer, which discharges the battery at a calibrated current, measuring how long it takes to reach the end-of-discharge voltage. This method can also show how the C-rate influences a battery’s effective capacity.
- At 1C, a battery ideally discharges in one hour, and the capacity is measured as 100%.
- At 2C, the battery discharges in 30 minutes, but due to internal losses (like heat generation), the capacity may drop to around 95% of its rated capacity.
- At lower C-rates (e.g., 0.5C), the battery may show a capacity above 100% because the discharge is slower, and internal losses are minimized.
Why Are Low C-Rates Used for Testing?
Most manufacturers test batteries at low C-rates to ensure longer discharge times and more reliable performance. For example, alkaline and lead-acid batteries are often rated at a low 0.05C (20-hour discharge). However, even under these conditions, lead-acid batteries typically don’t reach their full rated capacity because they are often overrated by manufacturers.
Testing at higher C-rates can reveal a battery’s real-world performance, which may be lower than expected due to heat and internal resistance. This is particularly relevant for applications where fast charging or discharging is required, such as in power tools, drones, and electric vehicles.
The Impact of C-Rate on Battery Types
Not all batteries react the same way to high C-rates. Here’s a quick look at how various battery types perform:
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Typically rated at 0.2C or 0.05C, these batteries are known for slower discharge times, and high discharge rates may significantly reduce their lifespan.
- Nickel-Based Batteries (NiCd, NiMH): These can handle higher C-rates, but they still have limits. At high discharge rates, their performance declines, and they may overheat.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Lithium-based batteries, such as LiFePO4 or NCM, have a more sophisticated design, allowing them to discharge at up to 1C (sometimes higher). Protection circuits are typically in place to prevent damage from excessive discharge rates.
- Advanced Lithium Chemistry (Nickel-Manganese): Some modern batteries made with nickel, manganese, and phosphate materials can withstand extreme C-rates, up to 10C, making them suitable for high-demand applications like electric vehicles and high-power devices.
How to Choose the Right C-Rate for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate C-rate for your battery depends on the application:
- Low-Current Applications: For devices like home appliances, where battery discharge happens over a long period, a lower C-rate (0.05C or 0.1C) is more suitable.
- High-Power Applications: For high-performance applications like drones or electric vehicles, higher C-rates (2C or 5C) are necessary to provide the quick bursts of power required.
- Balancing Efficiency and Longevity: Using a battery at too high a C-rate can shorten its lifespan due to excessive heat and internal resistance. It’s important to find a balance between discharge time and the health of the battery.
Conclusion
Understanding and selecting the right C-rate for your battery can dramatically improve performance and longevity. By choosing the right C-rate for your specific needs, whether it's for a slow, long-lasting discharge or a quick burst of power, you can ensure that your batteries work efficiently, reliably, and sustainably.
Popular Articles
Contact Details
Worktime :Monday to Friday 9am - 6pm (HKT)
WhatsApp/Wechat/Mobile :+8613645616165
Email : info@lifepo4cellstore.com
